Ptolemy I Of Egypt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ptolemy I Soter (; gr, Πτολεμαῖος Σωτήρ, ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'' "Ptolemy the Savior"; c. 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian and
/ref> Ptolemy's mother was
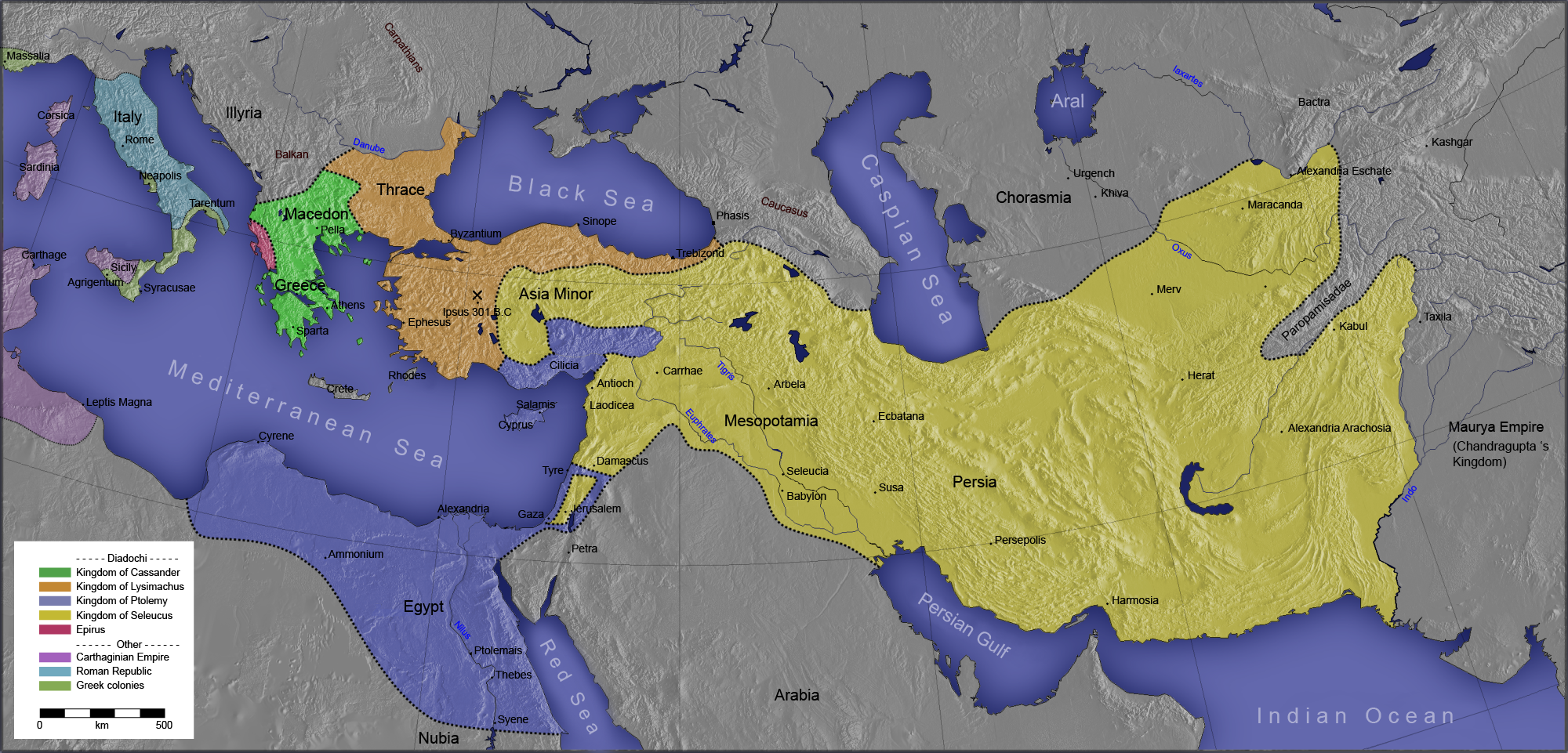 In 321 BC, Perdiccas attempted to invade Egypt, only to fall at the hands of his own men. Ptolemy's decision to defend the Nile against Perdiccas ended in fiasco for Perdiccas, with the loss of 2,000 men. This failure was a fatal blow to Perdiccas' reputation, and he was murdered in his tent by two of his subordinates. Ptolemy immediately crossed the Nile, to provide supplies to what had the day before been an enemy army. Ptolemy was offered the regency in place of Perdiccas; but he declined. Ptolemy was consistent in his policy of securing a power base, while never succumbing to the temptation of risking all to succeed Alexander.
In the long wars that followed between the different Diadochi, Ptolemy's first goal was to hold Egypt securely, and his second was to secure control in the outlying areas: Cyrenaica and Cyprus, as well as
In 321 BC, Perdiccas attempted to invade Egypt, only to fall at the hands of his own men. Ptolemy's decision to defend the Nile against Perdiccas ended in fiasco for Perdiccas, with the loss of 2,000 men. This failure was a fatal blow to Perdiccas' reputation, and he was murdered in his tent by two of his subordinates. Ptolemy immediately crossed the Nile, to provide supplies to what had the day before been an enemy army. Ptolemy was offered the regency in place of Perdiccas; but he declined. Ptolemy was consistent in his policy of securing a power base, while never succumbing to the temptation of risking all to succeed Alexander.
In the long wars that followed between the different Diadochi, Ptolemy's first goal was to hold Egypt securely, and his second was to secure control in the outlying areas: Cyrenaica and Cyprus, as well as
32
/ref> Ptolemy married once more to Berenice, Eurydice's cousin, who had come to Egypt as Eurydice's lady-in-waiting with the children from her first marriage to
17.11–12
, most notably in attributing a distinctly unheroic role in proceedings to Perdiccas. More recently, J. Roisman has argued that the case for Ptolemy's blackening of Perdiccas and others has been much exaggerated.

 *Ptolemy is portrayed by Anthony Hopkins and Elliot Cowan as the narrator and a main character in the historical epic ''Alexander'', directed by
*Ptolemy is portrayed by Anthony Hopkins and Elliot Cowan as the narrator and a main character in the historical epic ''Alexander'', directed by
Ptolemy Soter I at LacusCurtius
— (Chapter II of E. R Bevan's ''House of Ptolemy'', 1923)
(at Egyptian Royal Genealogy, with genealogical table)
Livius
by Jona Lendering
entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith
Alexander the Great {{DEFAULTSORT:Ptolemy 01 360s BC births 280s BC deaths 4th-century BC Pharaohs 3rd-century BC Pharaohs Pharaohs of the Ptolemaic dynasty Ancient Macedonian historians Ancient Eordaeans Hetairoi Historians who accompanied Alexander the Great Satraps of the Alexandrian Empire Somatophylakes Trierarchs of Nearchus' fleet 4th-century BC Greek people 3rd-century BC Greek people 4th-century BC Macedonians 3rd-century BC Macedonians 4th-century BC rulers 3rd-century BC rulers 3rd-century BC historians
companion
Companion may refer to:
Relationships Currently
* Any of several interpersonal relationships such as friend or acquaintance
* A domestic partner, akin to a spouse
* Sober companion, an addiction treatment coach
* Companion (caregiving), a caregive ...
of Alexander the Great from the Kingdom of Macedon in northern Greece who became ruler of Egypt, part of Alexander's former empire. Ptolemy was pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC to his death. He was the founder of the Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
, which ruled Egypt until the death
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in En ...
of Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
in 30 BC, turning the country into a Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
kingdom and Alexandria into a center of Greek culture.
Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. However, the latter is unlikely and may be a myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic Dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to Alexandria in a new tomb. Afterwards he joined a coalition against Perdiccas, the royal regent over Philip III of Macedon. The latter invaded Egypt but was assassinated by his own officers in 320 BC, allowing Ptolemy I to consolidate his control over the country. After a series of wars between Alexander's successors, Ptolemy gained a claim to Judea in southern Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, which was disputed with the Syrian king Seleucus I. He also took control of Cyprus and Cyrenaica, the latter of which was placed under the control of Ptolemy's stepson Magas. Ptolemy also had the Library of Alexandria
The Great Library of Alexandria in Alexandria, Egypt, was one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world. The Library was part of a larger research institution called the Mouseion, which was dedicated to the Muses, th ...
built.
Ptolemy I may have married Thaïs, his mistress during the life of Alexander; he is known to have married the Persian noblewoman Artakama Artakama (fl. 324 BC) was a Persian people, Persian noblewoman and the second wife of Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian general under Alexander the Great and the first Pharaoh of the Ptolemaic dynasty of Egypt.
Biography
Artakama (or as Plutarch calls ...
on Alexander's orders. He later married Eurydice, daughter of the Macedonian regent Antipater
Antipater (; grc, , translit=Antipatros, lit=like the father; c. 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general and statesman under the subsequent kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collaps ...
; their sons Ptolemy Keraunos and Meleager ruled in turn as kings of Macedon. Ptolemy's final marriage was to Eurydice's cousin and lady-in-waiting, Berenice I. Ptolemy I died in 282 BC and was succeeded by his son with Berenice, Ptolemy II
; egy, Userkanaenre Meryamun Clayton (2006) p. 208
, predecessor = Ptolemy I
, successor = Ptolemy III
, horus = ''ḥwnw-ḳni'Khunuqeni''The brave youth
, nebty = ''wr-pḥtj'Urpekhti''Great of strength
, gol ...
.
Early life and career
AGreek Macedonian Macedonian Greek or Greek Macedonian may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Macedonia (Greece), a region in Greece
*Macedonians (Greeks), the Greek people of Macedonia
* Greeks in North Macedonia, those living as a minority in the neighbo ...
, Ptolemy was born in 367 BC.Ptolemy I at Livius.org/ref> Ptolemy's mother was
Arsinoe Arsinoe grc, Ἀρσινόη, Arsinoë, pronounced Arsinoi in modern Greek, may refer to:
People
* Arsinoe of Macedon, mother of Ptolemy I Soter
* Apama II or Arsinoe (c. 292 BC–after 249 BC), wife of Magas of Cyrene and mother of Berenice II
...
. According to Satyrus the Peripatetic Satyrus ( grc-gre, Σάτυρος) of Callatis was a distinguished Peripatetic philosopher and historian, whose biographies of famous people are frequently referred to by Diogenes Laërtius and Athenaeus. He came from Callatis Pontica, as was learn ...
, Arsinoe was a descendant of Alexander I of Macedon
Alexander I of Macedon ( el, Ἀλέξανδρος ὁ Μακεδών), known with the title Philhellene (Greek: φιλέλλην, literally "fond/lover of the Greeks", and in this context "Greek patriot"), was the ruler of the ancient Kingdom of ...
and thus a member of the Argead dynasty, claiming ultimate descent from Heracles. Ostensibly, Ptolemy's father was Lagus, a Macedonian nobleman from Eordaea, but many ancient sources claim that he was actually an illegitimate son of Philip II of Macedon. If true, this would have made Ptolemy the half-brother of Alexander the Great. It is probable that this is a later myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic dynasty.
Ptolemy served with Alexander from his first campaigns, and was among the seven '' somatophylakes'' (bodyguards) of Alexander. He played a principal part in the later campaigns in Afghanistan and India. He participated in the Battle of Issus, commanding troops on the left wing under the authority of Parmenion. Later he accompanied Alexander during his journey to the Oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word '' ...
in the Siwa Oasis
The Siwa Oasis ( ar, واحة سيوة, ''Wāḥat Sīwah,'' ) is an urban oasis in Egypt; between the Qattara Depression and the Great Sand Sea in the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert, 50 km (30 mi) east of the Libyan Egypt–Li ...
where he was proclaimed a son of Zeus. Ptolemy had his first independent command during the campaign against the rebel Bessus
Bessus or Bessos ( peo, *Bayaçā; grc-gre, Βήσσος), also known by his throne name Artaxerxes V ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης; died summer 329 BC), was a Persian satrap of the eastern Achaemenid sa ...
whom his own guards captured and handed over to Ptolemy, who then handed him over to Alexander for execution.
Successor of Alexander
When Alexander died in 323 BC, Ptolemy is said to have instigated the settlement of the empire made atBabylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
. Through the Partition of Babylon
The Partition of Babylon was the first of the conferences and ensuing agreements that divided the territories of Alexander the Great. It was held at Babylon in June 323 BC.
Alexander’s death at the age of 32 had left an empire that stretched fro ...
, he was appointed satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with consid ...
of Egypt, under the nominal kings Philip III and the infant Alexander IV; the former satrap, the Greek Cleomenes Cleomenes may refer to:
* one of several kings of Sparta:
** Cleomenes I (c. 520 – c. 490 BC)
** Cleomenes II (370–309 BC)
** Cleomenes III (236–219 BC)
* Cleomenes of Naucratis (died 322 BC), Greek administrator
* Cleomenes the Cynic (c. 30 ...
, stayed on as his deputy. Ptolemy quickly moved, without authorization, to subjugate Cyrenaica.
By custom, kings in Macedonia asserted their right to the throne by burying their predecessor. Probably because he wanted to pre-empt Perdiccas, the imperial regent, from staking his claim in this way, Ptolemy took great pains in acquiring the body of Alexander the Great. On his deathbed, Alexander wished to be buried at the Temple of Zeus Ammon
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as (Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → (Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian ...
in the Siwa Oasis
The Siwa Oasis ( ar, واحة سيوة, ''Wāḥat Sīwah,'' ) is an urban oasis in Egypt; between the Qattara Depression and the Great Sand Sea in the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert, 50 km (30 mi) east of the Libyan Egypt–Li ...
of ancient Libya
The Latin name ''Libya'' (from Greek Λιβύη: ''Libyē'', which came from Berber: ''Libu'') referred to North Africa during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity. Berbers occupied the area for thousands of years before the recording of histor ...
instead of the royal tombs of Aigai in Macedon. However, his successors including Perdiccas attempted to bury his body in Macedon instead. In late 322 or early 321 BC, Alexander's body was in Syria, on its way to Macedon, when it was captured by Ptolemy I. He brought Alexander's remains back to Egypt, interring them at Memphis, but they were later moved to Alexandria where a tomb was constructed for them. Shortly after this event, Ptolemy openly joined the coalition against Perdiccas. Perdiccas appears to have suspected Ptolemy of aiming for the throne himself, and may have decided that Ptolemy was his most dangerous rival. Ptolemy executed Cleomenes for spying on behalf of Perdiccas; this removed the chief check on his authority, and allowed Ptolemy to obtain the huge sum that Cleomenes had accumulated.
Rivalry and wars
 In 321 BC, Perdiccas attempted to invade Egypt, only to fall at the hands of his own men. Ptolemy's decision to defend the Nile against Perdiccas ended in fiasco for Perdiccas, with the loss of 2,000 men. This failure was a fatal blow to Perdiccas' reputation, and he was murdered in his tent by two of his subordinates. Ptolemy immediately crossed the Nile, to provide supplies to what had the day before been an enemy army. Ptolemy was offered the regency in place of Perdiccas; but he declined. Ptolemy was consistent in his policy of securing a power base, while never succumbing to the temptation of risking all to succeed Alexander.
In the long wars that followed between the different Diadochi, Ptolemy's first goal was to hold Egypt securely, and his second was to secure control in the outlying areas: Cyrenaica and Cyprus, as well as
In 321 BC, Perdiccas attempted to invade Egypt, only to fall at the hands of his own men. Ptolemy's decision to defend the Nile against Perdiccas ended in fiasco for Perdiccas, with the loss of 2,000 men. This failure was a fatal blow to Perdiccas' reputation, and he was murdered in his tent by two of his subordinates. Ptolemy immediately crossed the Nile, to provide supplies to what had the day before been an enemy army. Ptolemy was offered the regency in place of Perdiccas; but he declined. Ptolemy was consistent in his policy of securing a power base, while never succumbing to the temptation of risking all to succeed Alexander.
In the long wars that followed between the different Diadochi, Ptolemy's first goal was to hold Egypt securely, and his second was to secure control in the outlying areas: Cyrenaica and Cyprus, as well as Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, including the province of Judea. His first occupation of Syria was in 318, and he established at the same time a protectorate over the petty kings of Cyprus. When Antigonus I
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( grc-gre, Ἀντίγονος Μονόφθαλμος , 'the One-Eyed'; 382 – 301 BC), son of Philip from Elimeia, was a Macedonian Greek nobleman, general, satrap, and king. During the first half of his life he se ...
, master of Asia in 315, showed expansionist ambitions, Ptolemy joined the coalition against him, and on the outbreak of war, evacuated Syria. In Cyprus, he fought the partisans of Antigonus, and re-conquered the island (313). A revolt in Cyrene was crushed the same year.
In 312, Ptolemy and Seleucus
Seleucus may refer to:
Monarchs and other people related to the Seleucid Empire
* Seleucus I Nicator (Satrap 311–305 BC, King 305 BC–281 BC), son of Antiochus and founder of the Seleucid Empire
* Seleucus II Callinicus (246–225 BC)
* Sele ...
, the fugitive satrap of Babylonia, both invaded Syria, and defeated Demetrius I, the son of Antigonus, in the Battle of Gaza. Again he occupied Syria, and again—after only a few months, when Demetrius had won a battle over his general, and Antigonus entered Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
in force—he evacuated it. In 311, a peace was concluded between the combatants. Soon after this, the surviving 13-year-old king, Alexander IV, was murdered in Macedonia on the orders of Cassander, leaving the satrap of Egypt absolutely his own master.
The peace did not last long, and in 309 Ptolemy personally commanded a fleet which detached the coastal towns of Lycia and Caria from Antigonus, then crossed into Greece, where he took possession of Corinth, Sicyon
Sicyon (; el, Σικυών; ''gen''.: Σικυῶνος) or Sikyon was an ancient Greek city state situated in the northern Peloponnesus between Corinth and Achaea on the territory of the present-day regional unit of Corinthia. An ancient mona ...
and Megara
Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, befo ...
(308 BC). In 306, a great fleet under Demetrius attacked Cyprus, and Ptolemy's brother Menelaus was defeated and captured in another decisive Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was ...
. Ptolemy's complete loss of Cyprus followed.
The satraps Antigonus and Demetrius now each assumed the title of king; Ptolemy, as well as Cassander, Lysimachus
Lysimachus (; Greek: Λυσίμαχος, ''Lysimachos''; c. 360 BC – 281 BC) was a Thessalian officer and successor of Alexander the Great, who in 306 BC, became King of Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedon.
Early life and career
Lysimachus was b ...
and Seleucus I Nicator, responded by doing the same. In the winter of 306 BC, Antigonus tried to follow up his victory in Cyprus by invading Egypt; but Ptolemy was strongest there, and successfully held the frontier against him. Ptolemy led no further overseas expeditions against Antigonus. However, he did send great assistance to Rhodes when it was besieged by Demetrius (305/304). The Rhodians granted divine honors to Ptolemy as a result of the lifting of the siege.
When the coalition against Antigonus was renewed in 302, Ptolemy joined it, and invaded Syria a third time, while Antigonus was engaged with Lysimachus in Asia Minor. On hearing a report that Antigonus had won a decisive victory there, he once again evacuated Syria. But when the news came that Antigonus had been defeated and slain by Lysimachus and Seleucus at the Battle of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus ( grc, Ἱψός) was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his so ...
in 301, he occupied Syria a fourth time.
The other members of the coalition had assigned all Syria to Seleucus, after what they regarded as Ptolemy's desertion, and for the next hundred years, the question of the ownership of southern Syria (i.e., Judea) produced recurring warfare between the Seleucid and Ptolemaic dynasties. Henceforth, Ptolemy seems to have involved himself as little as possible in the rivalries between Asia Minor and Greece; he lost what he held in Greece, but reconquered Cyprus in 295/294. Cyrenaica, after a series of rebellions, was finally subjugated in about 300 and placed under his stepson Magas.
Marriages, children, and succession
While Alexander was alive, Ptolemy had three children with his mistress Thaïs, who may also have been his wife: Lagus; Leontiscus; and Eirene, who was given in marriage to Eunostos of Soloi in Cyprus. During the Susa weddings, Ptolemy married Persian noblewomanArtakama Artakama (fl. 324 BC) was a Persian people, Persian noblewoman and the second wife of Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian general under Alexander the Great and the first Pharaoh of the Ptolemaic dynasty of Egypt.
Biography
Artakama (or as Plutarch calls ...
, as ordered by Alexander the Great. Around 322 BC
__NOTOC__
The denomination 322 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
In the pre-Julian Roman calendar, it was known as the Year ...
, he married Eurydice, daughter of Antipater
Antipater (; grc, , translit=Antipatros, lit=like the father; c. 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general and statesman under the subsequent kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collaps ...
, regent of Macedonia. They had five children before she was repudiated: three sons– Ptolemy Keraunos, king of Macedon from 281 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 281 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Barbula and Philippus (or, less frequently, year 473 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 281 BC for this year has b ...
to 279 BC
__NOTOC__
Year 279 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Publius Sulpicius Saverrio and Publius Decius Mus (or, less frequently, year 475 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination ...
; his brother and successor Meleager, who ruled for two months in 279 BC; and a 'rebel in Cyprus' who was put to death by his half-brother Ptolemy II
; egy, Userkanaenre Meryamun Clayton (2006) p. 208
, predecessor = Ptolemy I
, successor = Ptolemy III
, horus = ''ḥwnw-ḳni'Khunuqeni''The brave youth
, nebty = ''wr-pḥtj'Urpekhti''Great of strength
, gol ...
–as well as the daughters Ptolemais, who married Demetrius I of Macedon, and Lysandra, first married to Alexander V of Macedon
Alexander V of Macedon (Greek: Ἀλέξανδρος Εʹ ὁ Μακεδών; died 294, BC) was the second son of Cassander and Thessalonica of Macedon, who was a half-sister of Alexander the Great. He ruled as King of Macedon along with his broth ...
and after to Lysimachus' son Agathocles. Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives
Plutarch's ''Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans'', commonly called ''Parallel Lives'' or ''Plutarch's Lives'', is a series of 48 biographies of famous men, arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings, probably writt ...
'', "Demetrius"32
/ref> Ptolemy married once more to Berenice, Eurydice's cousin, who had come to Egypt as Eurydice's lady-in-waiting with the children from her first marriage to
Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularize ...
. Their children were Arsinoe II, Philotera, and Ptolemy II. Their eldest child Arsinoe married Lysimachus, then her half-brother Ptolemy Keraunos, and finally her full brother Ptolemy II.
In 285, Ptolemy made his son Ptolemy II his co-regent. His eldest legitimate son, Ptolemy Keraunos, fled to the court of Lysimachus. Ptolemy I died in January 282 aged 84 or 85. Shrewd and cautious, he had a compact and well-ordered realm to show at the end of forty years of war. His reputation for good nature and liberality attached the floating soldier-class of Macedonians and other Greeks to his service, and was not insignificant; nor did he wholly neglect conciliation of the natives. He was a ready patron of letters, founding the Great Library of Alexandria
The Great Library of Alexandria in Alexandria, Egypt, was one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world. The Library was part of a larger research institution called the Mouseion, which was dedicated to the Muses, th ...
. The Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
which he founded ruled Egypt for nearly three hundred years. It was a Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
kingdom known for its capital Alexandria, which became a center of Greek culture. Ptolemaic rule ended with the death of Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
in 30 BC.
Historian
Ptolemy himself wrote an eyewitness history of Alexander's campaigns (now lost). In the second century AD, Ptolemy's history was used byArrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; )
was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period.
''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best ...
of Nicomedia as one of his two main primary sources (alongside the history of Aristobulus of Cassandreia
Aristobulus of Cassandreia (c. 375 BC – 301 BC), Greek historian, son of Aristobulus, probably a Phocian settled in
Cassandreia, accompanied Alexander the Great on his campaigns. He served throughout as an architect and military engineer as wel ...
) for his own extant '' Anabasis'' of Alexander, and hence large parts of Ptolemy's history can be assumed to survive in paraphrase or précis in Arrian's work. Arrian cites Ptolemy by name on only a few occasions, but it is likely that large stretches of Arrian's ''Anabasis'' reflect Ptolemy's version of events. Arrian once names Ptolemy as the author "whom I chiefly follow", and in his Preface writes that Ptolemy seemed to him to be a particularly trustworthy source, "not only because he was present with Alexander on campaign, but also because he was himself a king, and hence lying would be more dishonourable for him than for anyone else".
Ptolemy's lost history was long considered an objective work, distinguished by its straightforward honesty and sobriety, but more recent work has called this assessment into question. R. M. Errington argued that Ptolemy's history was characterised by persistent bias and self-aggrandisement, and by systematic blackening of the reputation of Perdiccas, one of Ptolemy's chief dynastic rivals after Alexander's death. For example, Arrian's account of the fall of Thebes in 335 BC (''Anabasis'' 1.8.1–1.8.8, a rare section of narrative explicitly attributed to Ptolemy by Arrian) shows several significant variations from the parallel account preserved in Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
, most notably in attributing a distinctly unheroic role in proceedings to Perdiccas. More recently, J. Roisman has argued that the case for Ptolemy's blackening of Perdiccas and others has been much exaggerated.
Euclid
Ptolemy personally sponsored the great mathematician Euclid. He found Euclid's seminal work, the ''Elements
Element or elements may refer to:
Science
* Chemical element, a pure substance of one type of atom
* Heating element, a device that generates heat by electrical resistance
* Orbital elements, parameters required to identify a specific orbit of ...
'', too difficult to study, so he asked if there were an easier way to master it. According to Proclus
Proclus Lycius (; 8 February 412 – 17 April 485), called Proclus the Successor ( grc-gre, Πρόκλος ὁ Διάδοχος, ''Próklos ho Diádokhos''), was a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher, one of the last major classical philosophers ...
, Euclid famously quipped: "Sire, there is no Royal Road to geometry."
In art and fiction

 *Ptolemy is portrayed by Anthony Hopkins and Elliot Cowan as the narrator and a main character in the historical epic ''Alexander'', directed by
*Ptolemy is portrayed by Anthony Hopkins and Elliot Cowan as the narrator and a main character in the historical epic ''Alexander'', directed by Oliver Stone
William Oliver Stone (born September 15, 1946) is an American film director, producer, and screenwriter. Stone won an Academy Award for Best Adapted Screenplay as writer of '' Midnight Express'' (1978), and wrote the gangster film remake '' Sc ...
.
*Ptolemy appears as a minor character in Mary Renault's ''Alexander Trilogy'' novels.
See also
* History of Ptolemaic Egypt * Serapis, Greco-Egyptian god, promoted by PtolemyReferences
Citations
Sources
*Bibliography
* Walter M. Ellis: ''Ptolemy of Egypt'', London: Routledge. 1993. * Christian A. Caroli: ''Ptolemaios I. Soter – Herrscher zweier Kulturen'', Konstanz: Badawi. 2007. * *McKechnie, Paul and Jennifer A. Cromwell (eds). ''Ptolemy I and the Transformation of Egypt, 404–282 BCE''. Leiden, NL; Boston, MA: Brill, 2018. .External links
Ptolemy Soter I at LacusCurtius
— (Chapter II of E. R Bevan's ''House of Ptolemy'', 1923)
(at Egyptian Royal Genealogy, with genealogical table)
Livius
by Jona Lendering
entry in historical sourcebook by Mahlon H. Smith
Alexander the Great {{DEFAULTSORT:Ptolemy 01 360s BC births 280s BC deaths 4th-century BC Pharaohs 3rd-century BC Pharaohs Pharaohs of the Ptolemaic dynasty Ancient Macedonian historians Ancient Eordaeans Hetairoi Historians who accompanied Alexander the Great Satraps of the Alexandrian Empire Somatophylakes Trierarchs of Nearchus' fleet 4th-century BC Greek people 3rd-century BC Greek people 4th-century BC Macedonians 3rd-century BC Macedonians 4th-century BC rulers 3rd-century BC rulers 3rd-century BC historians